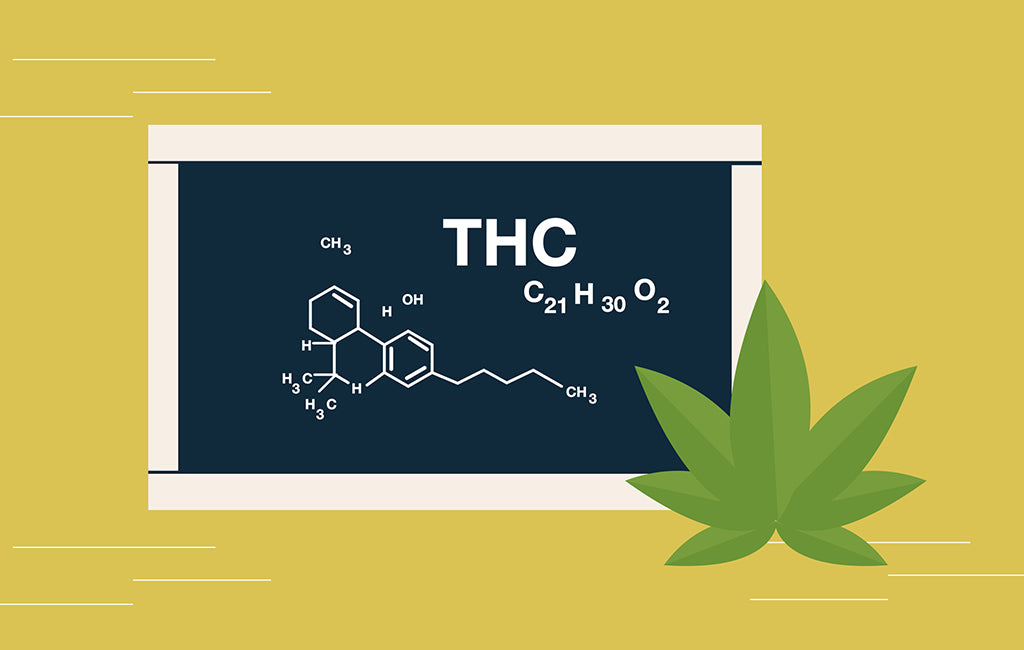
THC — known chemically as delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) — is a cannabinoid found in in marijuana, and its main psychoactive ingredient. But how does THC work? What are its benefits? And what is the difference between THC and CBD?
How THC Works
The human body contains a system of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors), lipids (fats, oils, waxes, certain vitamins, hormones, most of the non-protein cell membrane), and enzymes (naturally produced proteins that help support life) called the endocannabinoid system (ECS). In fact, all animals, including vertebrates (mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish) and invertebrates (sea urchins, leeches, mussels, nematodes, etc.) have an ECS.
... research over the years into the benefits of THC has been somewhat restrained and, on the federal level, cannabis that contains 0.3% THC or more is still illegal.
The purpose of the ECS is to maintain homeostasis — the process a living thing uses to maintain a stable condition necessary for survival. If homeostasis is not maintained, it results in death. The ECS regulates the various cardiovascular, nervous and immune system functions inside our cells. Our bodies produce endocannabinoids (similar to the cannabinoids in plants), which help keep everything running smoothly.
However, sometimes our bodies get out of whack (from poor diet, lack of exercise, too much stress, etc.), and the endocannabinoids are in dire need of reinforcement. That’s the role the cannabinoid THC (as well as the more than 113 cannabinoids in the cannabis plant such as CBD, CBG, CBN and CBC) plays in the overall well-being of our body and mind.
The Medicinal Uses of THC
One of the reasons THC has become so popular as a treatment for various medical conditions is that it’s a natural solution. That said, cannabis high in THC is still classified as a Schedule 1 drug, the same classification as heroin and L.S.D. This means that research over the years into the benefits of THC has been somewhat restrained and, on the federal level, cannabis that contains 0.3% THC or more is still illegal.
To give you an idea of the medicinal potential of THC, let’s look at the Compassionate Use Act of 1996 passed in California. By a 56% vote, the act was approved for “legalizing the use, possession, and cultivation of cannabis by patients with a physician's recommendation, for any illness for which marijuana provides relief.”
Like California, other states have passed laws making medical use and/or the recreational use of marijuana legal. You can access information about your state here.
Following are three more benefits (one new and two in more detail) of consuming cannabis with a high THC content:
Endocannabinoid Deficiency
Endocannabinoid deficiency is a theory first proposed in 2001 by Dr. Ethan Russo, director of research and development for the International Cannabis and Cannabinoids Institute. The idea is that your body doesn’t produce enough cannabinoids on its own, which results in an imbalance within the body’s homeostatic processes. It’s not known if endocannabinoid deficiency happens because of illness or mental distress, or whether it’s genetic. Because the ECS plays such a critical role in so many bodily functions (sleep, mood, clarity), not having enough cannabinoids can cause health problems and have lingering effects. It’s why many people have embraced cannabis high in THC, CBD and various other cannabinoids as part of their preventive health strategy.
Pain Relief
The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage.” In other words, it’s a warning that something is wrong. While it’s a good thing in that regard, it’s not something we want to experience for too long. One of THCs most recognized benefits is that it helps with pain relief. In the book Marijuana as Medicine: The Science Behind the Controversy, the author concluded that “after critically reviewing existing research on THC and pain relief, the IOM [Institute of Medicine] team concluded that cannabinoids can provide mild to moderate relief from discomfort.”
Appetite Stimulation
Next to getting you high, THC’s best-known effect is that it gives people “the munchies.” Why does THC increase your appetite? It’s thought to decrease your body’s level of a peptide (a compound consisting of two or more amino acids linked in a chain) called peptide tyrosine tyrosine (PYY). High levels of PYY increase your appetite; low levels decrease it. THC also increases ghrelin, which is famously known as the hunger hormone. Plus THC’s interaction with nerve cells, called pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons, may also play a role in promoting one’s appetite. Appetite stimulation can be a huge help to people with certain conditions.
The Difference Between THC and CBD
The most obvious difference between THC and CBD is that THC will get you high and CBD will not. Not only does CBD not get you high, but when taken together with THC, studies have shown that CBD may minimize some of the side effects of THC such as a rapid heartbeat, and impaired memory paranoia. If so, this is important because it means medical marijuana patients can tolerate higher doses of THC, which may result in a better health outcome.
Both THC and CBD have been shown to be beneficial in the reduction of pain, stomach discomfort, stress, tension and promote restful sleep. However, studies have revealed that THC may promote healthy vision and stimulate one’s appetite more effectively than CBD.
The side effects (all temporary) with THC include increased heart rate, coordination problems, dry mouth, red-eye, slower reaction times, memory loss and stress. It’s also thought that THC might be connected with long-term negative psychiatric issues (especially for adolescents who consume large amounts of it). CBD is well-tolerated even in large doses. If you experience side effects with CBD it’s more than likely due to CBD interacting with other medications you’re currently taking. CBD’s side effects may include fatigue, weight loss, dizziness, a change in appetite and diarrhea.
People often prefer to use CBD over THC because they are not interested in the euphoric effects of THC, and because the side effects of CBD are minimal compared with those of THC.
Zebra CBD: The Benefits of Delta-9 THC Without the ‘High’
If you’re looking for a nutraceutical to help alleviate stress, sleep issues or physical discomfort, CBD may be worth a try. All Zebra CBD products contain less than 0.3% delta-9 THC, so you get all the potential full-spectrum benefits of CBD without THC’s psychoactive effects. And with our 90-Day Money-Back Guarantee, you can sample any of our products risk-free. For anyone who gets a charge out a good deal, that’s a little bit of euphoria in itself.
Sources:
Scientific American. Marijuana Flips Appetite Switch in Brain
Sage Journals. Cannabidiol inhibits THC-elicited paranoid symptoms and hippocampal-dependent memory impairment









