From CBD muscle rub in many an athlete’s gym bag, to CBD cream for sale and CBD blood pressure tablets in Granny’s purse, people from all walks of life are starting to explore the benefits of CBD. So the questions arise: What does CBD affect in our bodies, our mood, our stress level or our appetite?
Scientists researching the effects of cannabis discovered the existence of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the mid-1990s. It has since been determined that this system not only exists in humans but also in animals.
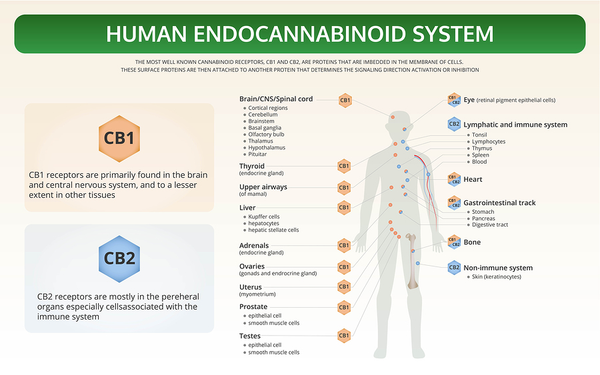
The endocannabinoid system (“endo” means internal; within) acts on multiple systems in the human body, including the cardiovascular, respiratory, reproductive and nervous systems. It oversees the majority of our physiological functions, affecting our sleep, appetite, memory and stress level. The ECS also plays a role in pain, inflammation, motor control, muscle formation, bone growth, liver function and reproduction (among others).
The ECS has two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, which are found mostly in the central nervous system; and CB2 receptors, which are found mostly in the peripheral nervous system. These receptors are activated by naturally occurring endocannabinoids.
Unfortunately, it’s easy to throw the endocannabinoid system out of whack. Your diet, how much you exercise, your stress level and other factors can take a toll. This is where CBD can help: Compounds in the cannabis plant interact positively with the endocannabinoid system, helping to restore homeostasis.
Biochemistry aside, simply put: The endocannabinoid system sends out endocannabinoid scouts called neurotransmitters to check whether everything is running smoothly. If it finds a problem, it sends out instructions on how to fix it — keeping the body in a state of homeostasis, or optimal function.
Experts aren’t 100% sure exactly how CBD interacts with the ECS. Many believe it prevents endocannabinoids from being broken down, increasing their effectiveness.